一、项目介绍
通过鸿蒙app连接华为云服务器远程控制arduino UNO R4 WIFI的LED矩阵。
项目结构分为三大部分:
1、华为云配置
2、arduino设备侧配置
3、鸿蒙app应用侧配置
二、设计思路
- 配置华为云服务器,包括了购买实例、创建产品、配置产品服务(属性与命令)、添加设备(获取设备唯一ID);
- 在MQTTX中模拟设备端,测试服务器的收发是否正常;
- 配置设备侧,将uno R4通过mqtt连接上华为云,此时已经可以通过华为云手动下发指令控制arduino;
- 通过DevEco编写鸿蒙APP,应用侧通过http请求连接上华为云,编写点击事件模拟平台对设备进行命令下发;
- 测试arduino设备与鸿蒙app间是否调通,测试任务能否正确完成。
三、系统流程图
四、软硬件介绍
1、设备侧
设备侧使用的是Arduino uno R4 WIFI
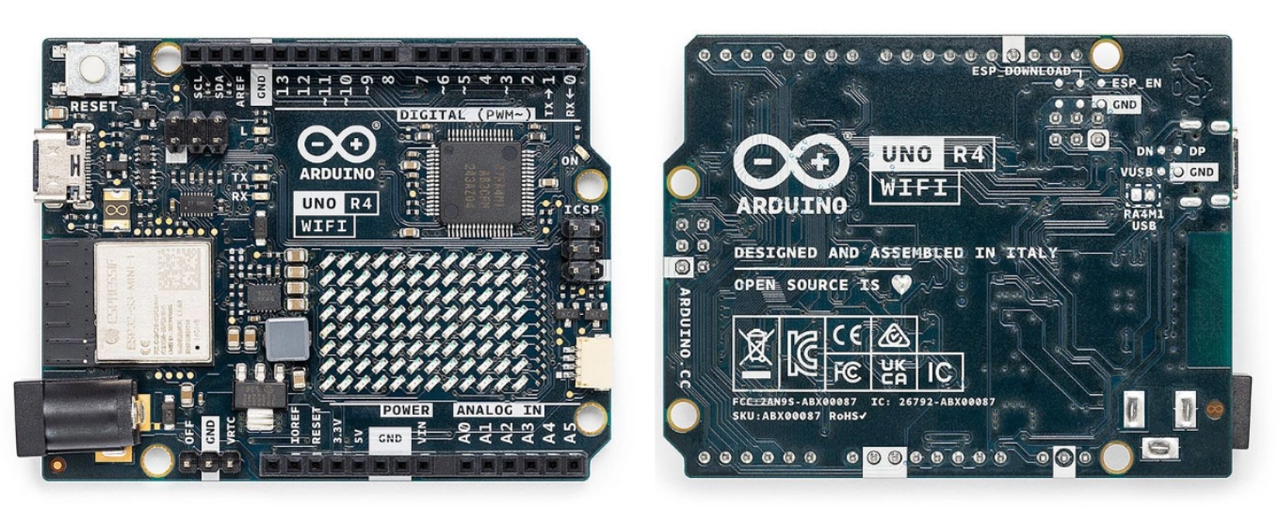
Arduino UNO R4 WiFi 将瑞萨电子的 RA4M1 微处理器与乐鑫的 ESP32-S3 相结合,为创客打造了一款一体化工具,具有增强的处理能力和多样化的全新外设。凭借其内置的 Wi-Fi® 和蓝牙®功能,UNO R4 WiFi 使制造商能够探索无限的创意可能性。此外,这款多功能板拥有方便的板载 12x8 LED 矩阵和 Qwiic 连接器。LED 矩阵是完全可编程的,可直接在电路板上制作视觉原型,为创新和释放创造力提供了充足的空间。通过 Qwiic 连接器,用户可以即插即用的方式创建项目。UNO R4 WiFi 为各个级别的创客提供了无与伦比的灵活性和可能性。
2、云服务器
本次服务器我选择了华为云,华为云提供了完善的配置参数和稳定的连接,在查看相关文档后发现其上手难度并不高,所以尝试尝试。
在本次项目实现后,我不由得承认,华为云已经可以作为成熟的IoT服务器供以创客们开发使用了。
3、应用侧
应用侧我基于DevEco Studio,开发了一款简易的鸿蒙app来连接华为云,远程控制连上云的设备。
HUAWEI DevEco Studio为开发者提供HarmonyOS应用开发所需的工程模板创建、代码编辑、编译、调试、发布等E2E的应用开发服务,支持多端应用开发、分布式多端调测、多端模拟仿真和全方位的质量与安全保障。具有以下能力特点:
- 多设备统一开发环境:支持多种HarmonyOS设备的应用/服务开发,包括手机(Phone)、平板(Tablet)、车机(Car)、智慧屏(TV)、智能穿戴(Wearable),轻量级智能穿戴(LiteWearable)和智慧视觉(Smart Vision)设备。
- 支持多语言的代码开发和调试:包括Java、XML(Extensible Markup Language)、C/C++ 、eTS(Extended TypeScript)、 JS(JavaScript)、CSS(Cascading Style Sheets)和HML(HarmonyOS Markup Language)。
- 支持FA(Feature Ability)和PA(Particle Ability)快速开发:通过工程向导快速创建FA/PA工程模板,一键式打包成HAP(HarmonyOS Ability Package)。
- 支持分布式多端应用/服务开发:一个工程和一份代码可跨设备运行,支持不同设备界面的实时预览和差异化开发,实现代码的最大化重用。
- 支持多设备模拟器:提供多设备的模拟器资源,包括手机、平板、车机、智慧屏、智能穿戴设备的模拟器,方便开发者高效调试。
- 支持多设备预览器:提供JS和Java预览器功能,可以实时查看应用/服务的布局效果,支持实时预览和动态预览;同时还支持多设备同时预览,查看同一个布局文件在不同设备上的呈现效果。
五、 华为云配置
1、服务器配置
1、购买实例
2、创建产品
1、创建产品
2、配置自定义模型,包括了服务中的属性和命令。(配置完成后的参数大概如图)
3、添加设备
1、注册设备
2、注册后点击详情,记住圈出的这些参数,后续需要在代码中添加
2、mqtt调试
使用mqtt客户端,此处我使用的MQTTX。
填入自己华为云服务器对应的参数,点击连接即可。成功连接后华为云的设备页面可以看的设备变为在线状态。
此时客户端模拟设备侧与华为云连接,可以收发报文来测试服务器的配置是否有无。
关于Topic的格式华为云官网有详细的定义。
3、获取身份认证
1、悬停右上角,点击我的凭证
找到对应你服务器所在地区的项目ID,后续代码中会使用
2、悬停右上角,点击统一身份认证
一定要新创建一个用户,和企业管理员用户区分开。记住新创建IAM用户的用户名与密码,后续要使用。
六、设备侧Arduino代码编写
1、初始化参数
首先在IDE中需要下载对应使用的库,我并没有采用uno4自带的<WiFiS3.h>,而是采取了esp32芯片的通用库<WiFi.h>。
值得一提的是<PubSubClient.h> 需要下载2.8.0版本,否则会报错。
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#include "Arduino_LED_Matrix.h"
#include "matrix_graph.h"
ArduinoLEDMatrix matrix;
WiFiClient espClient;
PubSubClient client(espClient);
const char* ssid = "****"; //wifi名称
const char* password = "****"; //wifi密码
const char* mqttServer = "*******"; //例如iot-mqtts.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com,详情参考华为云控制台
const int mqttPort = 1883; //例如1883(MQTT地址1883,MQTTS地址8883,详情参考华为云控制台)
//三元组
const char* ClientId ="*****";
const char* mqttUser ="******";
const char* mqttPassword = "**********";
//注册设备的ID和密钥
#define device_id "******"
#define secret "******"
//注意修改自己的服务ID
#define Iot_link_Body_Format "{\"services\":[{\"service_id\":\"LED_Control\",\"properties\":{%s"
//参考上报格式:{"services":[{"service_id":"LED_Control","properties":{"state": 30}}]}
//设备属性上报
#define Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_Report "$oc/devices/"device_id"/sys/properties/report"
//接收平台下发的命令
#define Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_Commands "$oc/devices/"device_id"/sys/commands/#"
//设备相应平台的命令
#define Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_CommandsRes "$oc/devices/"device_id"/sys/commands/response/request_id="
//改为你自己的"device_id"
//一些变量
String Property_Light = "Light";
int Light_temp=1;
long lastMsg = 0;
int led = LED_BUILTIN;
2、setup函数与loop函数
简单的配置arduino板上的外设,在setup中含有了wifi的连接
void setup() {
//wifi初始化
Serial.begin(115200); //
pinMode(led, OUTPUT); //配置LED为输出模式
matrix.begin();
matrix.clear();
Light_temp=0;
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.println("Connecting to WiFi..");
}
Serial.println("Connected to the WiFi network");
//MQTT初始化
MQTT_Init();
}
void loop() {
if (!client.connected()){
MQTT_Init();
}
else client.loop();
long now = millis();
}
3、MQTT初始化
链接上MQTT并且订阅对应的Topic
void MQTT_Init()
{
client.setServer(mqttServer, mqttPort);
client.setKeepAlive(60);
while (!client.connected())
{
Serial.println("Connecting to MQTT...");
if (client.connect(ClientId, mqttUser, mqttPassword ))
{
Serial.println("connected");
}
else
{
Serial.print("failed with state ");
Serial.print(client.state());
delay(3000);
}
}
client.setCallback(callback); //设定回调函数,当ESP8266收到订阅消息时会调用此方法
boolean res = client.subscribe(Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_Commands); //连接成功时订阅主题commands
if(res != true){ //如果订阅失败
Serial.println("mqtt subscribe topic [" + String(Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_Commands) + "] fail"); //打印订阅失败的消息
}
Serial.println("mqtt subscribe topic [" + String(Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_Commands) + "] ok"); //打印订阅成功的消息
Serial.println("MQTT Connected OK!"); //打印连接成功的消息
}
在串口中会打印目前的项目进程,随时了解哪一步出现了问题
4、上报函数MQTT_POST
void MQTT_POST(int Data)
{
char properties[32]; //定义一个字符数组,用于存储属性数据
char jsonBuf[128]; //定义一个字符数组,用于存储JSON数据
sprintf(properties,"\"Light\":%d}}]}",Data); //生成属性数据
sprintf(jsonBuf,Iot_link_Body_Format,properties); //生成JSON数据
client.publish(Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_Report, jsonBuf); //使用MQTT客户端将JSON数据发送到指定的主题
Serial.println(Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_Report); //打印主题
Serial.println(jsonBuf); //打印JSON数据
Serial.println("MQTT Publish OK!"); //打印成功消息
}
调用此函数用于向平台发送报文。
5、回调函数callback
只要设备接收到了平台发来的报文,便立即执行回调函数。
//回调函数
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length)
{
String recdata=""; //定义一个字符串,用于存储接收到的消息
Serial.println("接收到订阅的消息:主题为:");
Serial.println(topic); //打印主题
Serial.println("数据内容:");
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
{
recdata+=(char)payload[i]; //将接收到的消息转换为字符串
}
Serial.println(recdata); //打印接收到的消息
//解析JSON数据
DynamicJsonDocument jsonBuffer(1024); //创建一个JSON文档对象
deserializeJson(jsonBuffer,recdata); //将接收到的消息解析为JSON格式
JsonObject obj = jsonBuffer.as<JsonObject>(); //将JSON文档对象转换为JSON对象
String com = obj["paras"]; //获取paras字段的值
Serial.println("解析命令:");
Serial.println(com); //打印解析后的命令
deserializeJson(jsonBuffer,com); //将命令解析为JSON格式
obj = jsonBuffer.as<JsonObject>(); //将JSON文档对象转换为JSON对象
String ledcom = obj["state"]; //获取led字段的值
Serial.println("解析LED命令:");
Serial.println(ledcom); //打印解析后的LED命令
//解析request id,设备响应时的topic需要包含命令的request id,且会动态变化
char *p=topic; //定义一个字符指针,指向主题
String request_id=""; //定义一个字符串,用于存储request id
int i=0; //定义一个整数,用于存储主题的长度
while((*p++)!='\0') //获取主题的长度
{
i++;
}
topic+=(i-36); //移动指针位置,指向request id
for(int j=i-36;j<i;j++) //获取request id
request_id+=*topic++;
Serial.println("request_id:"+request_id); //打印request id
Serial.println("命令设备响应"); //打印响应消息
String param="{}"; //定义一个字符串,用于存储响应消息
client.publish((Iot_link_MQTT_Topic_CommandsRes+request_id).c_str(),param.c_str()); //使用MQTT客户端将响应消息发送到指定的主题
if(ledcom == "0")
{
Light_temp = 0;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_0, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为0%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "10")
{
Light_temp = 10;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_10, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为10%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "20")
{
Light_temp = 20;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_20, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为20%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "30")
{
Light_temp = 30;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_30, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为30%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "40")
{
Light_temp = 40;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_40, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为40%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "50")
{
Light_temp = 50;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_50, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为50%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "60")
{
Light_temp = 60;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_60, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为60%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "70")
{
Light_temp = 70;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_70, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为70%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "80")
{
Light_temp = 80;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_80, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为80%"); //打印开灯消息
}
else if(ledcom == "90")
{
Light_temp = 90;
matrix.clear();
matrix.renderBitmap(percent_90, 8, 12);
Serial.println("亮度调整为90%"); //打印开灯消息
}
if(Light_temp == 0)
{
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN,LOW); //熄灯
Serial.println("关灯"); //打印关灯消息
}
else
{
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN,HIGH); //亮灯
Serial.println("开灯"); //打印开灯消息
}
MQTT_POST(Light_temp); //上报参数
}
此段代码可以大致分为三部分,第一部分为解析收到的报文,将报文中需要的数据提取出;第二部分为回传,因为华为云平台要求平台下发命令后设备需要回传,需要分析命令后的id号并即时的回传;第三部分为逻辑判断,根据命令报文回传的数据来操作arduino板的片上外设。
在串口监视器中,我们可以观测到数据流转的详细情况:
首先接收消息,其次分析解析命令,然后设备响应,最后回传报文。
6、LED矩阵库函数
矩阵的各个状态点阵图。
//arduino_secrets.h header file
extern uint8_t grid[8][12] = {
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_0[8][12] = {
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_10[8][12] = {
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_20[8][12] = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_30[8][12] = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_40[8][12] = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_50[8][12] = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_60[8][12] = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_70[8][12] = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_80[8][12] = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
};
extern uint8_t percent_90[8][12] = {
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
};
具体现象展示:
七、应用侧鸿蒙app代码编写
1、配置Models文件与Tools文件
①HW_User.ets
export class HW_User {
auth: Auth
constructor(name: string, password: string, domain: string) {
this.auth = {
"identity": {
"methods": [
"password"
],
"password": {
"user": {
"domain": {
"name": domain //IAM用户所属账号名
},
"name": name, //IAM用户名
"password": password //IAM用户密码
}
}
},
"scope": {
"domain": {
"name": domain //IAM用户所属账号名
}
}
}
}
}
interface Auth {
identity: Identity
scope: Scope
}
interface Identity {
methods: string[]
password: Password
}
interface Password {
user: User
}
interface User {
name: string
password: string
domain: Domain
}
interface Domain {
name: string
}
interface Scope {
domain: Domain
}
②HttpTool.ets
import { http } from '@kit.NetworkKit'
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit'
export class HttpTool {
static get(url: string, fn: Function) {
// 每一个httpRequest对应一个HTTP请求任务,不可复用
let httpRequest = http.createHttp()
let options: http.HttpRequestOptions = {
method: http.RequestMethod.GET,
// 当使用POST请求时此字段用于传递请求体内容,具体格式与服务端协商确定
expectDataType: http.HttpDataType.OBJECT, // 可选,指定返回数据的类型
// 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段
// header: { 'Accept': 'application/json' },
header: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'X-Auth-Token': globalThis.token //获取云端数据需要xToken认证,这里使用全局变量
},
}
httpRequest.request(url, options, (err: BusinessError, data: http.HttpResponse) => {
if (!err) {
fn(data)
} else {
console.info('error:' + JSON.stringify(err))
}
httpRequest.destroy()
})
}
//一般情况下的post请求
static post(url: string, param: string | Object | ArrayBuffer, fn: Function) {
// 每一个httpRequest对应一个HTTP请求任务,不可复用
let httpRequest = http.createHttp()
let options: http.HttpRequestOptions = {
method: http.RequestMethod.POST,
// 当使用POST请求时此字段用于传递请求体内容,具体格式与服务端协商确定
extraData: param,
expectDataType: http.HttpDataType.OBJECT, // 可选,指定返回数据的类型
// 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段
// header: { 'Accept': 'application/json' },
header: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
}
httpRequest.request(url, options, (err: BusinessError, data: http.HttpResponse) => {
if (!err) {
fn(data)
} else {
console.info('error:' + JSON.stringify(err))
}
httpRequest.destroy()
})
}
//命令下发使用的post请求
static postCommands(url: string, param: string | Object | ArrayBuffer, fn: Function) {
// 每一个httpRequest对应一个HTTP请求任务,不可复用
let httpRequest = http.createHttp()
let options: http.HttpRequestOptions = {
method: http.RequestMethod.POST,
// 当使用POST请求时此字段用于传递请求体内容,具体格式与服务端协商确定
extraData: param,
expectDataType: http.HttpDataType.OBJECT, // 可选,指定返回数据的类型
// 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段
// header: { 'Accept': 'application/json' },
header: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'X-Auth-Token': globalThis.token //下发命令需要xToken认证,这里使用全局变量
},
}
httpRequest.request(url, options, (err: BusinessError, data: http.HttpResponse) => {
if (!err) {
fn(data)
} else {
console.info('error:' + JSON.stringify(err))
}
httpRequest.destroy()
})
}
}
2、登录界面
简单的ui,登录界面的编写,将token的获取封装进了登录按钮的点击事件。
import router from '@ohos.router'
import { HW_User } from '../Models/HW_User'
import { HttpTool } from '../Tools/HttpTool'
import { http } from '@kit.NetworkKit'
@Entry
@Component
@Preview
struct First{
@State message: string = '登录'
@State account: string = ''
@State password: string = ''
@State allow:boolean = false
@State upload:boolean = true
private url: string = "https://iam.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/v3/auth/tokens"
// private hw_user = new HW_User('你创建的IAM用户', '你的IAM用户密码', '你的登录或注册的默认用户就是domain')
private hw_user = new HW_User('zxc', 'zxc123', 'hw084741351')
build() {
Column(){
Column() {
Text("点个小灯")
.fontColor('#096789')
.fontSize(70)
}
.height('36%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
Column()
{
Row()
{
// 用户名输入框
TextInput({ placeholder: this.account===''? "请输入您的用户名":this.account })
.type(InputType.Normal)
.width('80%')
.height(50)
.placeholderColor(Color.Black)
.backgroundColor('#ffd3d7d3')
.borderRadius(10)
.margin({ bottom: 10})
.onChange(val=>{
this.account=val
console.log(val)
})
}
Blank()
Row()
{
// 密码输入框
TextInput({ placeholder: this.password===''?"请输入您的密码":this.password })
.type(InputType.Password)
.width('80%')
.height(50)
.placeholderColor(Color.Black)
.backgroundColor('#ffd3d7d3')
.borderRadius(10)
.onChange(val=>{
this.password=val
console.log(val)
})
}
Blank()
Blank()
Blank()
Row()
{
//登录按钮
Button("登录")
.margin({top:20})
.width(130)
.height(50)
.fontColor(Color.White)
.fontSize(25)
.onClick(async () => {
{
HttpTool.post(this.url, this.hw_user, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result))
globalThis.token = data.header['x-subject-token'] //x-subject-token作为全局变量,让封装的HttpTool类可以使用
// 使用封装类后的HttpTool的post请求获取到x-token的值
})
router.pushUrl({
url: "pages/Index"
})
}
})
.backgroundColor('#096789')
.borderStyle(BorderStyle.Dotted)
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly)
}
.width("100%")
.height("30%")
}
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}
点击登录按钮的同时,也获取了当前用户的token,供以接下来的华为云连接。
3、控制界面
import { HW_User } from '../Models/HW_User'
import { HttpTool } from '../Tools/HttpTool'
import { http } from '@kit.NetworkKit'
interface Command {
service_id: string
command_name: string
paras: Paras
}
interface Paras {
state: string
// Light: string
}
interface Properties {
Light: string
}
// Command和Paras使用接口来实现命令下发的上传格式,Properties是使用接口获取云端数据的返回数据
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
private endpoint: string = 'bf95ab7125.st1.iotda-app.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com'
private project_id: string = '166f44f0228a4b92bcdcd1273d19e3fa'
private device_id: string = '6768fd6b2ff1872637c9e2cd_FIRST'
//endpoint是你之前复制的https接入地址,project_id是你复制的api凭证(要与区域保持一致),device_id是你的设备id
private url1: string =
'https://' + this.endpoint + '/v5/iot/' + this.project_id + '/devices/' + this.device_id + '/shadow'
private url2: string =
'https://' + this.endpoint + '/v5/iot/' + this.project_id + '/devices/' + this.device_id + '/commands'
//url1是获取云端数据的写法,url2是命令下发的写法
@State properties: Properties = { Light: '' }
//使用接口重载可以方便后续的调整
private com0: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '0' } }
private com1: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '10' } }
private com2: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '20' } }
private com3: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '30' } }
private com4: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '40' } }
private com5: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '50' } }
private com6: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '60' } }
private com7: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '70' } }
private com8: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '80' } }
private com9: Command = { service_id: 'LED_Control', command_name: 'LightUP', paras: { 'state': '90' } }
@State light: number = 0
build() {
Column() {
// Blank()
Text("亮度")
.fontSize(50)
.margin({ top:30,bottom:0})
.fontColor(Color.White)
Text(this.light.toFixed())
.fontColor(Color.White)
.fontSize(100)
.margin({ top:3,bottom: 50})
Column() {
Row() {
Button('开灯')
.height(100)
.margin({right:40})
.width(100)
.backgroundColor('#ffa98fb1')
.borderStyle(BorderStyle.Dotted)
.fontSize(25)
.onClick(() => {
this.light = 30
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com3, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
})
Button('关灯')
.height(100)
.width(100)
.backgroundColor('#ffa98fb1')
.borderStyle(BorderStyle.Dotted)
.fontSize(25)
.onClick(() => {
this.light = 0
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com0, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
})
}.margin({ top:10,bottom: 10})
Column() {
Row() {
Button('+')
.height(100)
.margin({ right: 40 })
.width(100)
.backgroundColor('#ffa98fb1')
.borderStyle(BorderStyle.Dotted)
.fontSize(50)
.onClick(() => {
this.light += 10
if(this.light < 0)
this.light = 0
if(this.light > 100)
this.light = 100
switch (this.light)
{
case 0:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com0, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 10:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com1, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 20:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com2, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 30:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com3, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 40:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com4, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 50:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com5, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 60:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com6, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 70:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com7, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 80:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com8, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 90:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com9, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
}
})
Button('-')
.height(100)
.width(100)
.backgroundColor('#ffa98fb1')
.borderStyle(BorderStyle.Dotted)
.fontSize(50)
.onClick(() => {
this.light -= 10
if(this.light < 0)
this.light = 0
if(this.light > 100)
this.light = 100
switch (this.light)
{
case 0:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com0, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 10:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com1, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 20:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com2, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 30:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com3, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 40:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com4, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 50:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com5, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 60:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com6, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 70:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com7, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 80:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com8, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
case 90:
HttpTool.postCommands(this.url2, this.com9, (data: http.HttpResponse) => {
console.log('result:', JSON.stringify(data.result)) //将获取到的命令返回结果打印到终端上
})
break;
}
})
}.margin({ top:10, bottom: 100 })
}
}
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}
八、项目结果展示
1、默认上电并app登录用户
应用侧:
输入用户名密码登陆成功后,日志中会显示成功获取到的token。
云服务器:
设备状态显示在线
设备侧:
WIFI连接成功,MQTT连接成功。
实物:
电源指示灯亮,LED灯以及LED矩阵均全熄灭。
2、开灯指令
应用侧:
单击“开灯”按钮
云服务器:
在设备详情里的消息追踪里可以观测命令的下发是否成功。下图我们可以看到,开灯指令下发成功,并且设备端也即时的回传了响应后的设备属性。
服务器里的设备属性也会同步变换。
设备侧:
设备收到平台下发的命令,解析命令并执行,且上报给平台设备当前的属性。
实物:
开灯默认亮度为30%
3、关灯指令
关灯指令与开灯指令类似,此处就不再过多赘述。
部分现象如下:
4、亮度调整
此处以亮度由80变90为例。
点击“+”,将亮度设置为90。
实物:
当亮度超过90%后,矩阵将显示太阳的模样。
